A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
Femoro-Femoral Bypass Graft
The femoral-femoral bypass graft connects the femoral arteries via a graft. It is usually performed due to an occlusion above the placed graft, enabling blood supply to the lower extremity.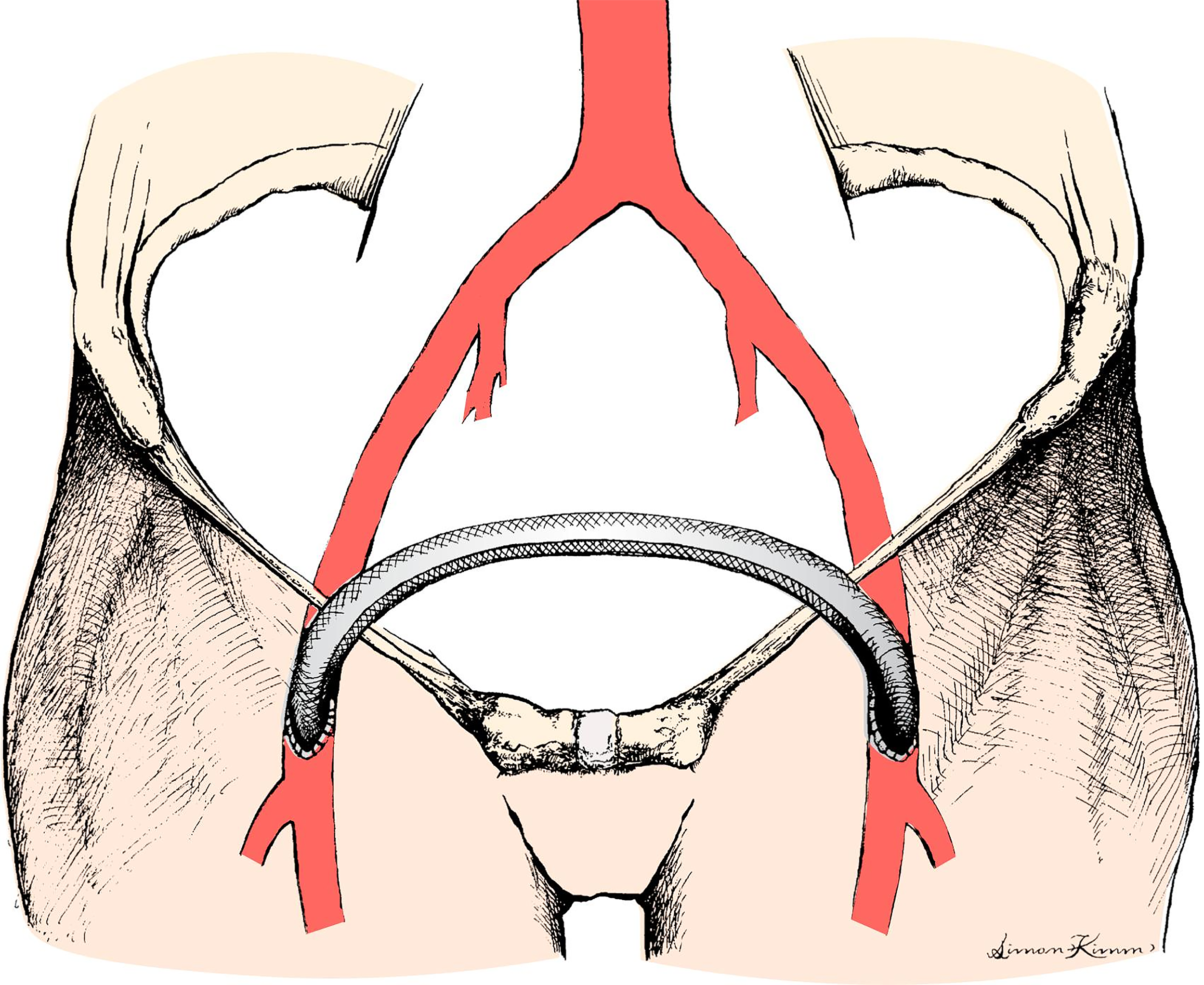
Presenting symptoms
Ischemic lower extremity - may see gangrene, ulceration, or pain at rest
It may be used to alleviate functional ischemia associated with claudication or exercise
Patients may present with a history of severe PVD, CAD, HTN, COPD, and DM
Three types of occlusive vascular disease
Type 1 - isolated to the aortic and iliac bifurcations
- No CAD
Type 2 - diffuse pattern involving coronary and cerebral circulations
- Higher incidence of HTN, DM
Type 3 - involves small vessels, especially lower limbs
Surgical procedure
Graft placed between unobstructed inflow source - common femoral, superficial, or deep femoral artery to target artery
Organ Considerations
Respiratory
Vascular patients often have a history of smoking and COPD
May have pulmonary function testing done preop to evaluate pt for GA versus regional
Cardiovascular
May see elevated morbidity and mortality if there is a history of CAD and HTN
Monitor ECG for LVH (Peaked R waves)
Neurological
May have cerebrovascular disease
- Document any deficits
Endocrine
DM associated with peripheral and autonomic neuropathies, silent MI, delayed gastric emptying
Check blood glucose as needed
Renal
There is a higher incidence of renal artery disease and renal insufficiency in this population
Check BMP
Hematologic
Ask about bruising tendency
May be on anti-platelet medication
Check CBC, PT, PTT
Position
Supine position
Keep the head in a neutral position
Massage/reposition the head during lengthy procedures to prevent alopecia
Heels off mattress for more prolonged procedures
Decreased FRC and HR
Increased venous return, leading to increased preload and CO
Increased intraabdominal pressure
Zone 3 (a-v-A) in the dorsal portion of the lungs
CNS: blood/cerebrospinal fluid drainage is gravity-dependent, valve-less
When supine = increased ICP, which decreases cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP= MAP-ICP/or CVP)
BMI elevated - decreased FRC. Difficulty maintaining tidal volumes due to body weight pressing down on the chest
Padding: Protect pressure points. Arms either with hands supinated <90degree (prevent Brachial Plexus injury from stretch) or alongside with hands facing body. Pad to prevent ulnae nerve injury. Possibly place a pillow under the knees if there is a history of back pain, maintain the lordotic curve in the spine, and prevent tension on the sciatic nerve. Prevent alopecia with padding of the head
Check eyes - always tape them to prevent corneal abrasion
Preoperative Considerations
Antibiotics
Cefazolin as per surgeon
Surgical time
2-3 hrs
EBL
200-300 mL
Age range
>55 yr, male: female 4:1
Morbidity
MI - 5-12%, respiratory insufficiency 5%, infection 2-5%, amputation 2-4%, CVA <1%
Mortality
2-4%
Pain score
4-6
Anesthetic considerations
Preoperatively
Pt ID, verify consent, NPO, history, allergies, airway assessment, and medications. Review chart. Type and screen - possible type and cross?
Questions answered
Consider GETA vs. epidural depending on the history
Have NTG and Neo drips in the room
Monitors
Pulse ox, ECG (II for dysrhythmias, V5 for ischemia), NIBP, Temp
2 large bore IVs
A-line?
Fluid warmers?
Bair huggers upper
Foley - U/O > 0.5 mL/kg/hr
Heparin 50-100 units/kg given IV before catheter manipulation
- Monitor ACT to prevent blood clots
Induction - GETA
Hemodynamic stability is essential - slow, gradual induction (avoid ischemia)
Preoxygenation
Zemuron 5 mg IV to minimize myalgias from Succinylcholine
Lidocaine 1 mg/kg/IV
Propofol 1-2 mg/kg/IV – if cardiac history, use Amidate 0.2-0.4 mg/kg/IV (2mg/mL vial)
Fentanyl 1-3 mcg/kg/IV
Succinylcholine 0.5-1.5 mcg/kg/min
Tape eyes as soon as eye lash reflex is gone, then intubate
Epidural
This addition can be used for post-op pain management - lidocaine 2% with 1/200,000 epinephrine or 0.5% bupivacaine is used. Titrate to the required level (T8-T10)
Maintenance
Consider modified hypotension to minimize bleeding, monitor ACT
Isoflurane - if smoker consider Sevo (less irritant)
Fentanyl
Start Hydromorphone for post-op pain management 0.5-2 mg (0.01-0.04 mg/kg)
Emergence
Prevention of HTN and tachycardia
Esmolol to control tachycardia on emergence
- 25-100 mg (0.5-2.0 mg/kg) May repeat every 5 min. (10 mg/mL)
Zofran 4 mg
Reverse Heparin if needed, with protamine 1 mg/100 units of heparin
- Watch for protamine reaction
- HOTN
- Histamine release and vasodilation
- Anaphylactoid reaction
- History of fish allergy, vasectomy, prior exposure (NPH insulin or surgery)
- Severe pulmonary vasoconstriction
- HOTN, increased pulmonary artery pressures, right heart failure
- HOTN
Complications
HTN, hypothermia (causes vasoconstriction), hemorrhage