A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
Lacrimal duct probe
Cause
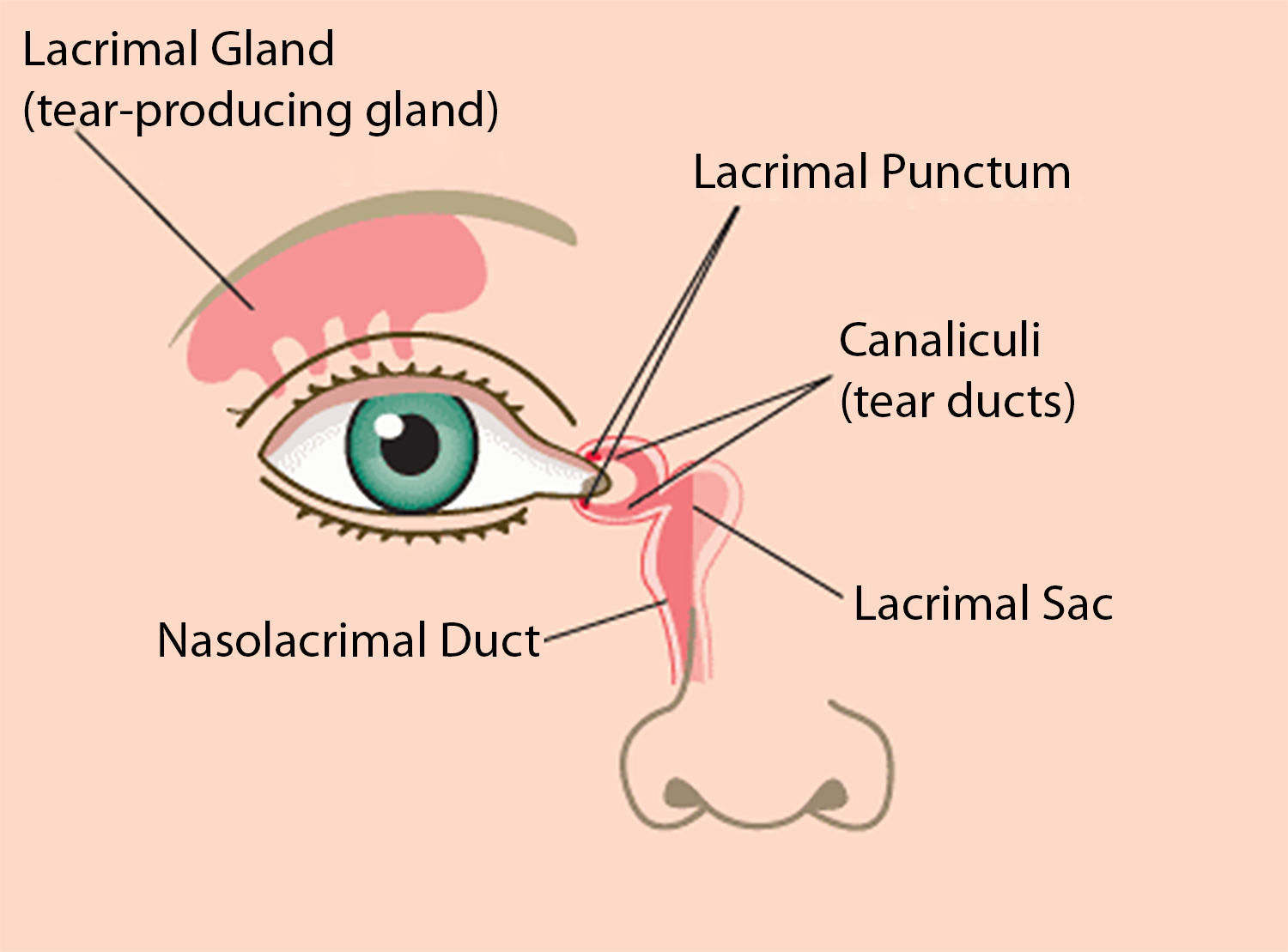 Being born with an underdeveloped tear-duct system can lead to tear-duct blockage, excess tearing, and infection. In infants, it usually resolves by age one. Eyelids move tears across the eyes. Tears keep the eyes lubricated and clean and contain antibodies that protect the eyes from infection.
Being born with an underdeveloped tear-duct system can lead to tear-duct blockage, excess tearing, and infection. In infants, it usually resolves by age one. Eyelids move tears across the eyes. Tears keep the eyes lubricated and clean and contain antibodies that protect the eyes from infection.
Excessive tears move down the lacrimal sac to the nasolacrimal duct and drain into the back of the nose.
It's the nasolacrimal duct that's involved in tear-duct blockage.
Causes of blocked tear ducts
Congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction or dacryostenosis
Most commonly, an infant is born with a duct that is too narrow or has a web of tissue blocking the duct and, therefore, doesn't drain properly or become blocked easily
Other causes could be cysts, nasal growth, or trauma
Symptoms
Excessive tearing and pus in the corner of the eyes
Surgical Treatments
Placement of probe under general anesthesia
A thin, blunt metal wire is gently passed through the tear duct to open any obstruction. Sterile saline is then irrigated through the duct into the nose to ensure an open path. There's minimal discomfort after the probing, which takes about 10 minutes
Another option is silicone tube placement, which involves stretching the tear ducts
- The tubes are usually left in place for 6 months
A newer form of treatment is balloon catheter dilation, in which a balloon is inserted through an opening in the corner of the eye and into the tear duct
Both procedures are relatively short but require that a child be put under anesthesia. They are generally successful, with an approximate 80% to 90% success rate in younger kids.
Anesthetic considerations
Immobile patient
Use of LMA
Monitor for oculocardiac reflex