A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
Post Operative Nausea and Vomitting (PONV)
Primary risk factors
Patient-specific
Female Gender
Nonsmoker
History of PONV
History of motion sickness
Anxiety
Anesthetic Related
Use of volatile anesthetics
Use of nitrous oxide
Use of etomidate/ketamine
Intra/postoperative use of opioids
High dose neostigmine (increased peristalsis)
PPV with ventilation >20 mmHg (open lower esophageal sphincter)
Surgery related
Duration of surgery
Types of surgery
- Laparoscopy, laparotomy, ear, eye mandibles, plastic, neurologic, abdominal, GYN and T&A surgeries
Anesthetic Considerations
Premedication
Zantac 150 mg PO
- H2 blocker - blocks Histamine = decreased acid production in the stomach, reduced hydrogen release from parietal cells
- Other drugs are cimetidine, famotidine
Reglan 10 mg PO
- 0.1 mg/kg for children
- Increases motility/LES tone and may have a central antiemetic effect by blocking dopaminergic receptors in the brain) - peaks 40-120 min post-administration
Reglan 10 mg IM
- 0.1mg/kg for children
- Should be given 45 min before surgery
Reglan 10-20 mg IV
- 0.15-0.2 mg/kg in children over 3-5 min at least 30-45 min before surgery
Alka-Seltzer Gold 2 tabs with 30 mL of water
- 0.4 mL, where the goal is to increase stomach PH to >2.5 before intubation
- Decreases the severity of aspiration pneumonia
Consider a Scopolamine patch before surgery
- 2-4 hr onset, dry mouth, drowsiness, contact dermatitis, visual disturbances
- Good hand washing after application and removal
Elevate the head during intubation
Consider cricoid pressure and perform RSI
Insert NG tube post-intubation to manage GI secretions
Chemoreceptor locations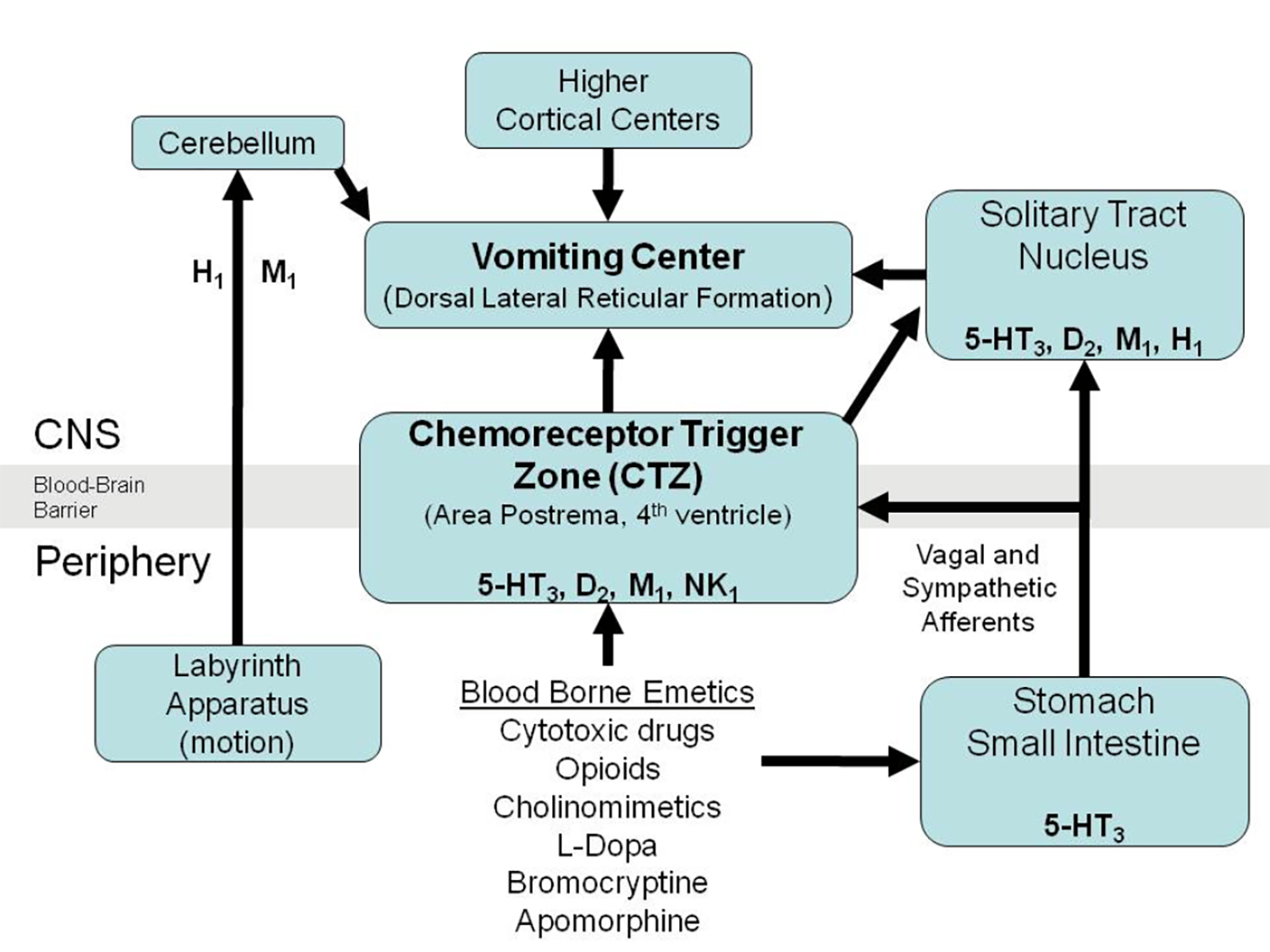
Cerebellum: H1, M1
Chemoreceptor trigger zone: 5HT3, D2, M1, NK1
Solitary tract nucleus: 5HT3, D2, M1, H1
Stomach/small intestine: 5HT3
5HT3: Ondansetron, Granisetron, Dolasetron, Palonosetron, Alosetron
D2: Prochlorperazine (Compazine), Promethazine (Phenergan), Droperidol, Metoclopramide
NK1: Aprepitant
M1: Scopolamine
H1: Diphenhydramine, Promethazine, Meclizine (Antivert)
Vomiting Center
Receptors and Associated Drugs
Serotonin/ 5HT receptor
- Approximately 80 percent of the human body's total serotonin is located in the Enterochromaffin cells in the gut where it is used to regulate intestinal movements
- Serotonin activates vagal afferents via the 5-HT3 receptor, which signals to the brain, generating nausea
- Zofran is an antagonist of the 5-HT3 receptor
Dopamine D2 receptor
- Part of the Chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) in the medulla, which communicates with the vomiting center
- Antagonists are Reglan, Phenergan, Compazine, Vistaril, Droperidol
Histamine H1 receptor
- Benadryl
Muscarinic M1 (acetylcholine)
- Scopolamine
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Dronabinol (from cannabis may alleviate nausea)
Spinal Accessory – Aprepitant
- Emend is an antiemetic chemical compound known as a Substance P antagonist
- Mediates its effect by blocking Neurokinin 1 receptor, preventing nausea and vomiting
Gastric Proton-Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Omeprazole (Prilosec)
- Inhibition of gastric acid secretion, longer action than H2-receptor antagonists
- Can give 40 mg IV post-induction, as effective as ranitidine in raising gastric pH >2.5
Lanzoprazole (Prevacid) and Rabeprazole (Aciphex)
- 20 mg and 30 mg, respectively, not as effective as Ranitidine 150 mg po
Pantoprazole (Protonix)
- 40 mg IV comparable with ranitidine 50 mg IV in increasing pH and reducing gastric fluid volume
Histamine H2 receptor
Cimetidine
- 300 mg IV helps reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration
Famotidine
- 20 mg IV given 15-30 min before surgery increases gastric pH
Ranitidine
- 50-100 mg IV decreases the risk associated with pulmonary aspiration