A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
Turbinate Resection
Etiology
The inferior turbinate is the largest of the nasal turbinates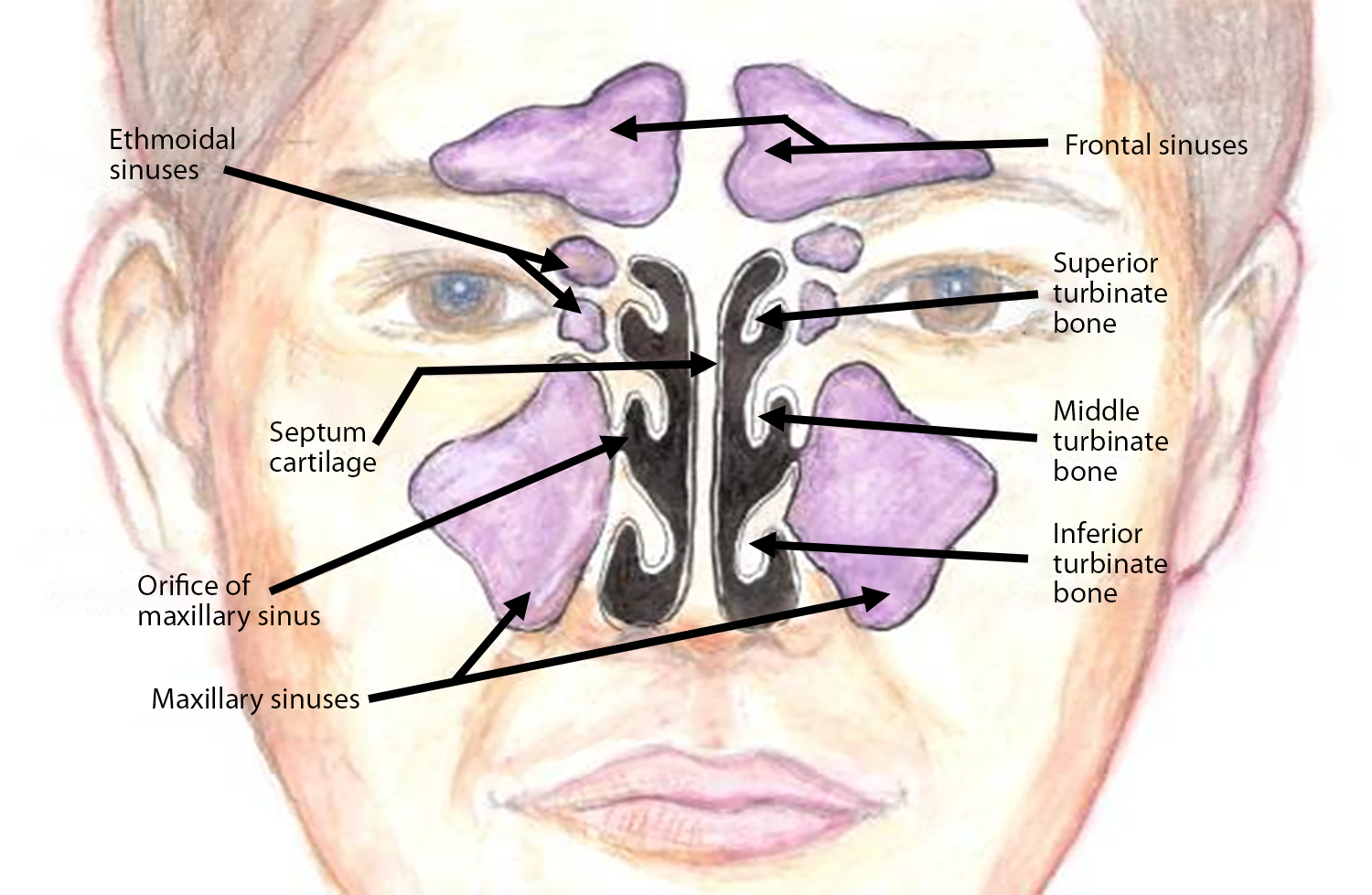
- Inferior, middle, superior
It can cause nasal obstruction when hypertrophied.
Various reduction options include radiofrequency ablation, cauterization, submucosal resection, partial resection, and out-fracture (to create a larger space for air to travel). At the conclusion, the cut edges are cauterized.
Adverse Events
Bleeding, usually controlled with cautery or nasal packing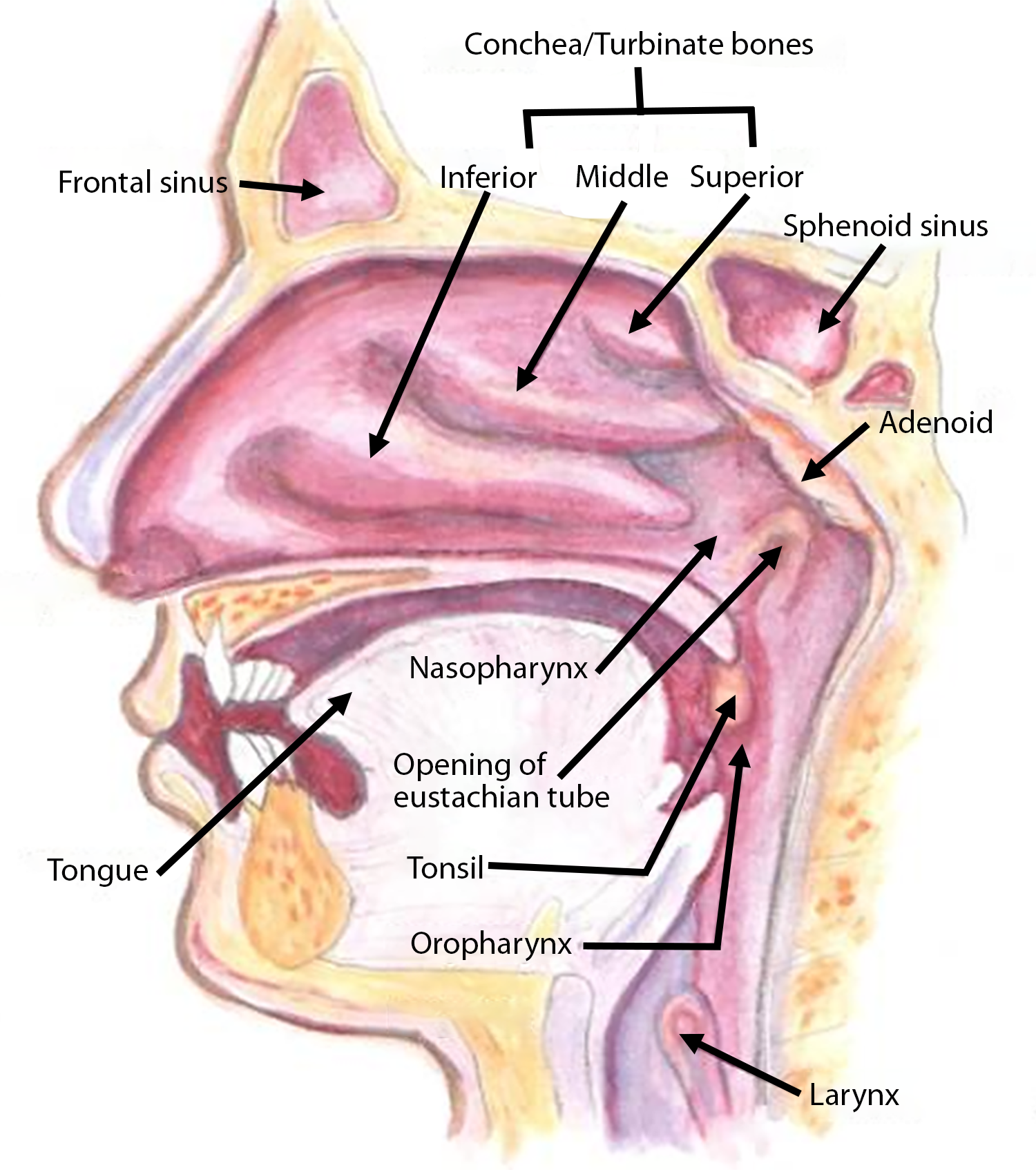
Anesthetic Considerations
Head elevated to 15-30 degrees
The table may turn 90-180 degrees
SPB on the lower side to minimize bleeding
Risk of airway fire with cautery - low FiO2
Risk of N/V due to possible aspiration of blood
Consider Decadron to minimize post-op edema (8 -12 mg IV)
No ketorolac due to the risk of microvascular bleeding
Oral RAE taped midline
Patient immobility
Clear surgical field
Smooth emergence to avoid post-op hemorrhage