A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
Mitral Regurgitation
Problem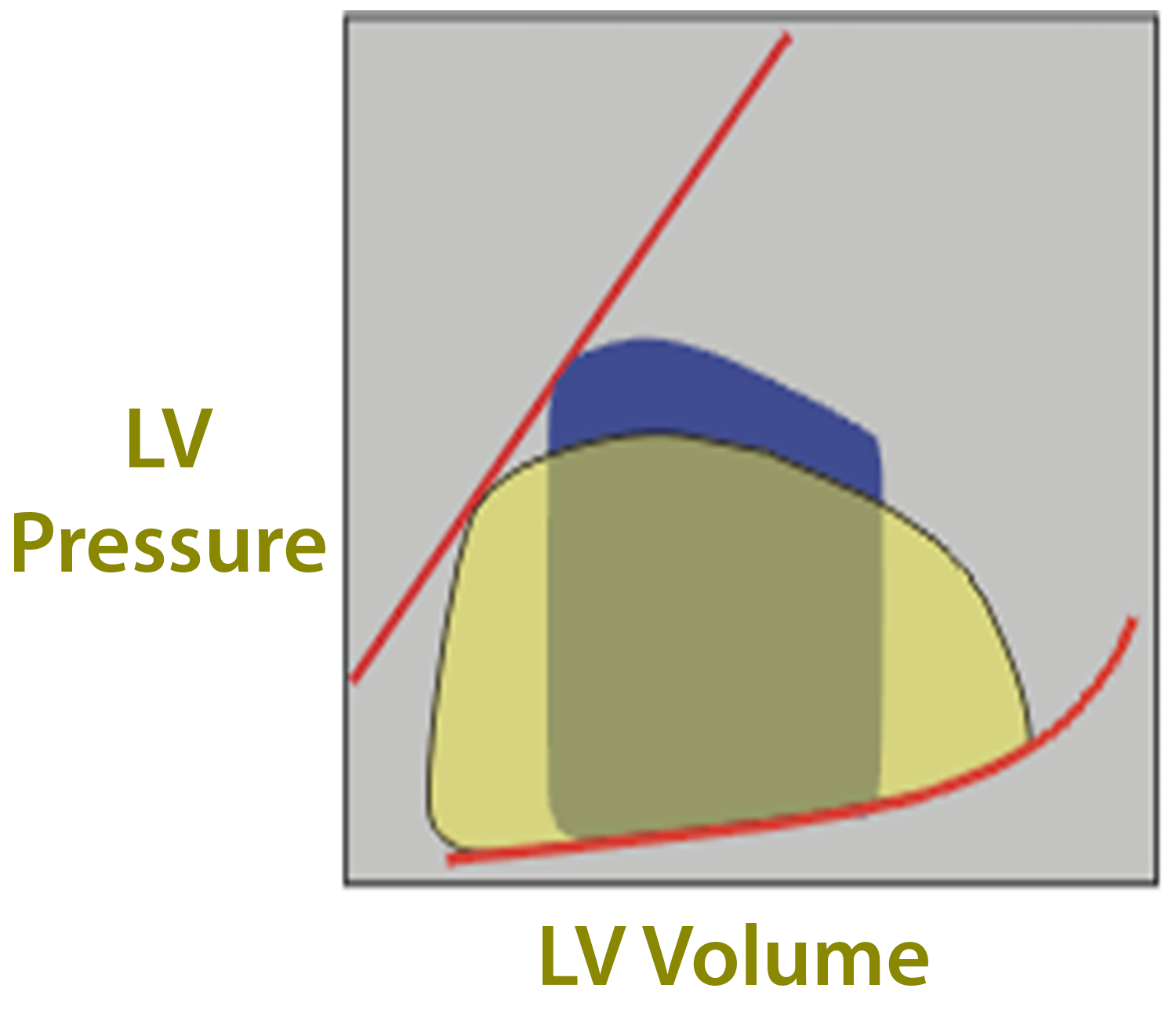
During systole - backflow to LA
- Increased LVEDV, LVEDP, and decreased LVESV
What to Optimize
LV Preload
Maintain
HR
SR 80-90, avoid bradycardia
Contractility
Maintain constant
SVR
Avoid increases, decrease to decrease MR, facilitate forward flow
PVR
Avoid increases
Etiology
Acute MR
- Rupture Chordae Tendineae
- Papillary Muscle dysfunction - MI/Ischemia
Chronic MR
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Mitral valve prolapse (20-70%)
- Chronic ischemic heart disease with cardiomyopathy and remodeling
- Endocarditis
- Annular dilation due to LV dilation
- Myxoma (syncope episodes)
- Congenital
Symptoms
Dyspnea, PND, orthopnea
Fatigue
Pulmonary HTN, RV failure
Hemoptysis
Systemic embolization in A-fib
Acute MR
Sudden volume overload of LA with pulmonary edema
Compensatory: Increase contractility, tachycardia, increase MVO2= LV failure, RVF
Chronic MR
Mild - asymptomatic with comp. changes
Moderate – symptomatic
Severe - terminal
Preoperative Considerations
- Fatigue and malaise (decreased CO)
- Holosystolic murmur, S3 gallop
- A-fib
- EKG - Left atrial enlargement in chronic
- ECHO - etiology and severity, use of color Doppler flow
- PAP
- V wave
- Overestimate LVEDP
- PAEDP best estimate for LVEDP
- Increase risk of PA perforation with pulmonary HTN
Surgical Technique
MV Replacement
Bioprosthetic valve
- No anticoagulation
- Life expectancy less
Mechanical Valve
- Life expectancy unlimited
- Anticoagulation
MV Repair
Valvuloplasty
No anticoagulation
Preserve LVEF
Surgical Technique
Median sternotomy with bicaval cannulation
CPB 28-32 C