A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
Mitral Stenosis
Problem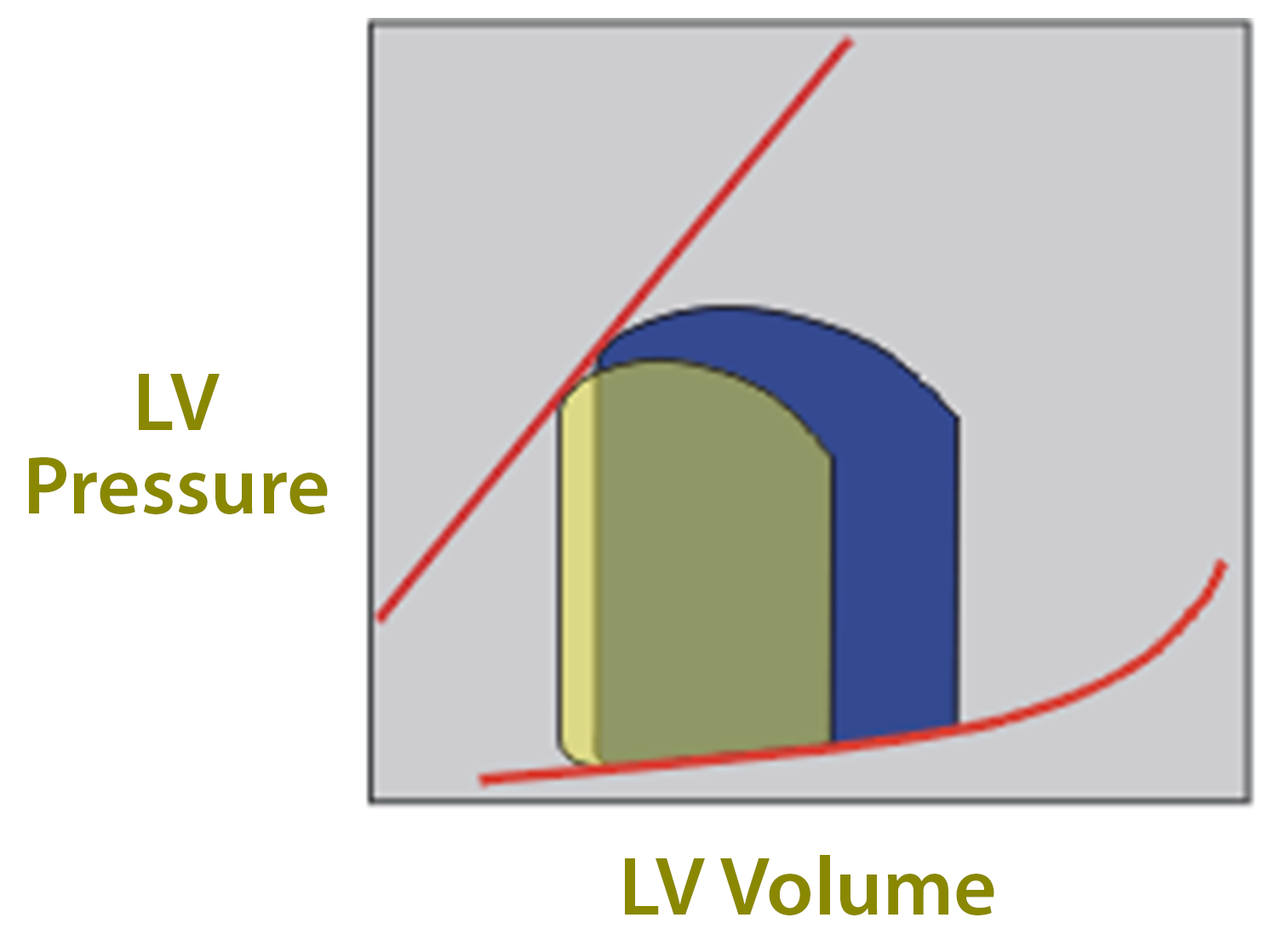
In diastole - decreased flow from LA
- Decreased LV volumes, SV, and LVEDP
What to Optimize
LV Preload
Maintain forward flow
HR
65-80, maintain NSR, avoid tachycardia
Contractility
Maintain
SVR
Maintain
PVR
Avoid increase, avoid hypercarbia, hypoxemia, acidosis, hypothermia
Anatomy
2 leaflets
Attached to papillary muscles by chordae tendineae
Anterior leaflet (next to outflow tract - note systolic anterior motion SAM)
Posterior leaflet
Valve area 4-6 cm2
- Mild MS: asymptomatic with compensation, valve area 1.5-2.5 cm2
- Moderate MS: A-fib with decreased CO, valve area <1-1.5 cm2
- Severe MS: terminal, valve area <1 cm2
Etiology
- Secondary to rheumatic heart disease (RHD) with scarring and fibrosis
- Women>men
- Often MR and AR if RHD
- Congenital or degenerative
Surgical indication
NYHA class III or IV symptoms (1.5-2.5 cm2)
Valve area <1 cm2 (critical) or emboli
Symptoms
Left atrial enlargement
Pulmonary edema
Dyspnea
PND
Fatigue
Palpitations - A-fib common
RHF with severe MS
Tricuspid regurgitation
LVF due to restructuring of chordae tendineae
Preop Considerations
- Diastolic murmur
- EKG - LAH, prominent a-waves, A-fib
- ECHO - Evaluate valve area, detect thrombus
PAWP
Overestimate LVEDP (use TEE to estimate)
Large a-wave
Increased risk for PA perforation with pulmonary HTN
Surgical Therapy
Balloon Valvuloplasty
Mitral valve replacement
Open mitral commissurotomy
Mechanical/bioprosthetic
Surgical Technique
Median sternotomy or lateral thoracotomy
+/-Bicaval cannulation - venous if transseptal to MV
CPB with temp 28-32 C
Post bypass
- PAP and PVR will usually decrease
- Persistent Pulmonary HTN
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
- Avoid an increase in PVR
- Severe Pulmonary HTN - Nitric Oxide
- Maintain afterload
- Treat SV arrhythmias
- Maintain LV and RV Functions