A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
One Lung Ventilation
Ventilate one lung to create a quiet field for the surgeon
Indications
Absolute Indications
Isolation of one lung due to purulent secretions/massive pulmonary hemorrhage
Control of distribution of ventilation
- Bronchopleural fistula, blebs, unilateral hypoxemia, unilateral lavage
Relative Indications
Surgical exposure
- Thoracic aortic aneurysm, pneumonectomy, upper lobectomies, procedures on the thoracic spine, esophageal resection, Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
Preoperative Evaluation
Respiratory risk factors
- Smoking, air pollution, industrial chemical exposure
Possible COPD
- Hyperinflation of lung tissue - may have increased PVR - possible R heart failure
Cancer patients - the 4Ms
- Mass effects
- Obstructive pneumonia, lung abscess, superior vena cava syndrome, tracheal distortion, recurrent laryngeal nerve or phrenic nerve paresis, chest wall abnormalities
- Metabolic effects
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome (muscle weakness due to decreased release of Ach), hypercalcemia, hyponatremia, Cushing syndrome (increased cortisol production)
- Metastases
- To the brain, bone, liver, and adrenals
- Medications
- Chemotherapy-induced lung changes
- Bleomycin
- Chemotherapy-induced lung changes
Nutritional status - may have low albumin
CXR
ECG - right ventricular hypertrophy and strain
ABG - preoperative hypoxemia with SpO2<90% can be predictive of post-op complications
Pulmonary function tests
Low-risk patients
- FEV1 >2 L or 80% of predicted
- Predicted postoperative (PPO) function test FEV1 >40%
- VO2 max >20 mL/kg/min
- Ability to climb five flights of stairs (indicates maximal oxygen consumption
High-risk patients
- FEV1 <0.7-2 L
- Predicted PPO <40%
- Carbon monoxide diffusion capacity <40-60% (sources vary)
- VO2 max <10 mL/kg/min
- Inability to climb one flight of stairs
Treat infections, excess bronchial secretions, bronchospasm, and nutritional deficiencies
Encourage the stoppage of smoking before surgery, if possible, to optimize patient outcomes
Double Lumen Tubes (DLT)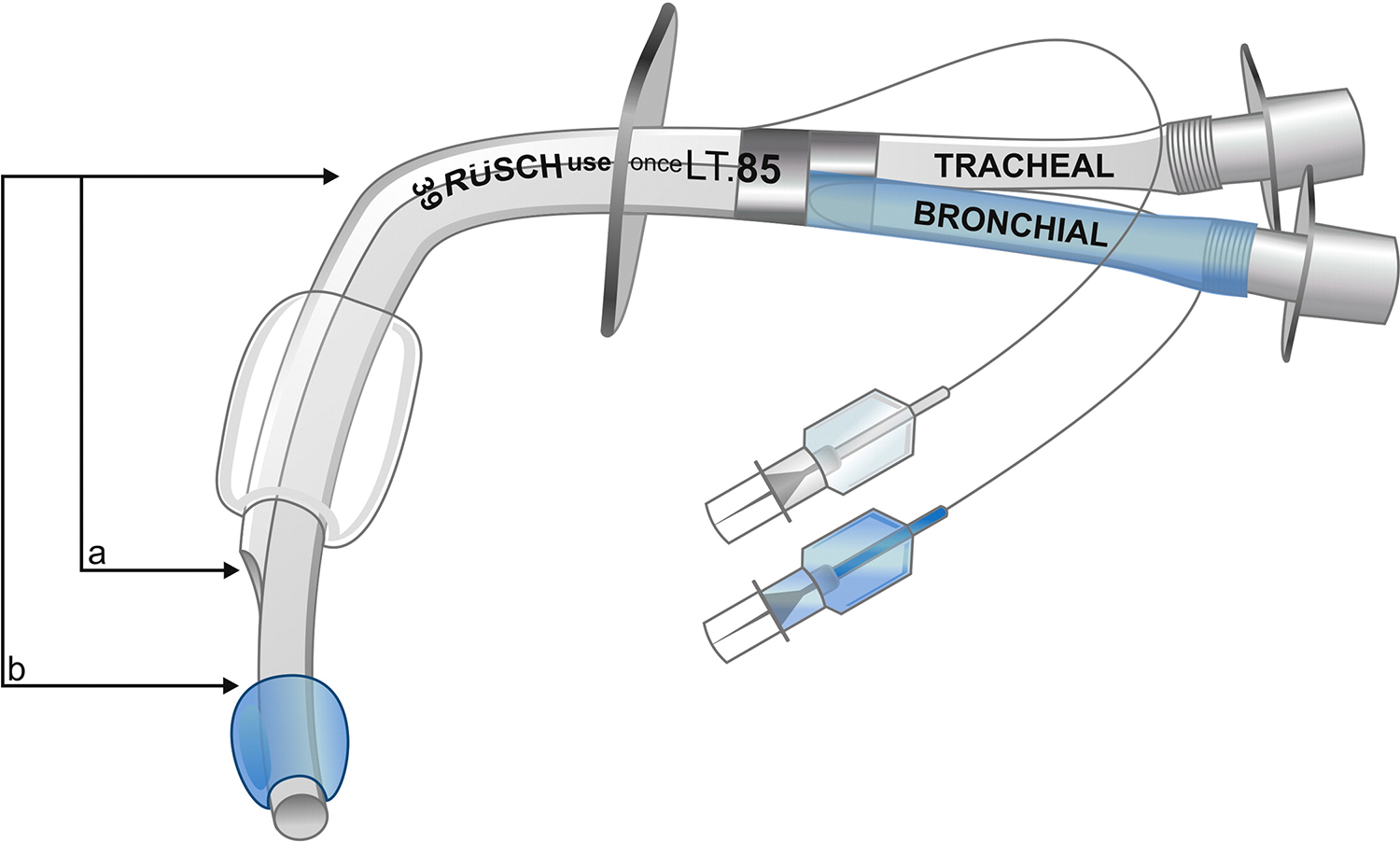
One lumen reaches the mainstem bronchus - blue cuff
- BB - blue for bronchus
One lumen ends in the trachea - clear cuff
Left is safer than right due to the takeoff of the upper lobe
- L = 5 cm
- R = 2 cm from the carina
Sizes
Left 41, 39, 37, 35, 28, 26
Right 41, 39, 37, 35
Female
<63 inches (160 cm)
- Size 35
>63 inches
- Size 37
Male
<67 inches (170 cm)
- Size 39
>67-inch
- Size 41
Always have sizes above and below
Insertion
Lubricate the distal end, including the cuff, use a MAC blade, insert until black ring through cords, remove the stylet, and rotate 90 degrees towards the bronchus you want to intubate
Depth
- 29 cm +/- 1 cm for every 10 cm of height above or below 170 cm
Tracheal cuff 5-10 mL of air, bronchial 1-2 mL of air
Placement
Check placement - both auscultation and fiber-optically
- Bilateral breath sounds with both cuffs inflated
- Clamp the tracheal side and open it to air - should only have breath sounds on the bronchial side
- Close the port and unclamp
- Repeat with the bronchial side - should only have breath sounds on the tracheal side.
Ways to Improve HPV (Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction)
Narcotic Anesthesia
CPAP 5-10 cm to the non-ventilated lung - improve oxygenation
PEEP 5-10 cm to the ventilated lung - stents airways open
Early ligation of pulmonary artery - pneumonectomy only
Periodic inflation of non-ventilated lung
Insufflation of oxygen into the collapsed lung
Limit MAC to <1
Reduce vasodilator usage - Cardene is the best option if needed
Postoperative Complications after Lung Resection
Arrhythmia
Myocardial infarction
Pulmonary embolism
Pneumonia and empyema