A small compilation of nurse anesthesia care plans
These anesthesia care plans are meant to inspire nurse anesthesia residents when they are making their care plans. Always make sure you fully understand and "own" your care plan. Your plan must be specific for your patient and should always be with the most up-to-date information.
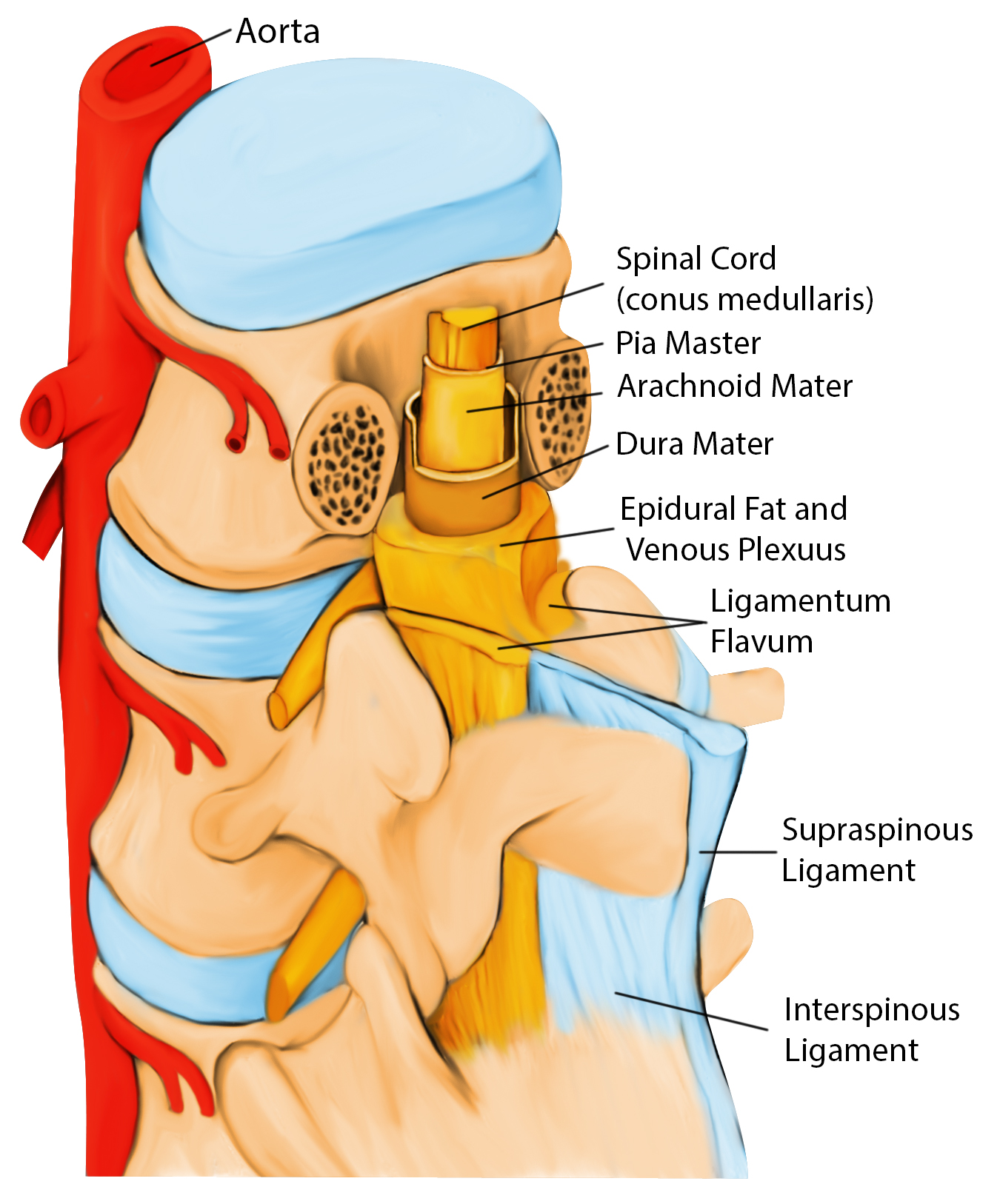
Spinal Neuraxial Block
Indications
Procedures below the umbilical
- Such as hernia repairs, gynecological and urologic, and lower extremity surgeries
C-Sections
Patients with congestive heart failure, except those with stenotic valvular heart disease or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which is contraindicated
Contraindications
Patient refusal
Infection at site
Coagulation defects
Sepsis
Neurologic disease, particularly involving the spinal cord, such as myelitis
Intracranial hypertension
Severe spinal or spinal cord deformity
Stenotic heart valve lesions
Severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Lack of anesthesiologist experience
Placement
Preload the patient with a minimum of 1 L fluids to prevent hypotension pre-placement
The distal termination of the spinal cord varies from about the level of the 3rd lumbar vertebrae (L3) in infants to the lower border of L1 in adults
Prepare patient, obtain consent, and do BP supine before sitting pt up to have a baseline
L3-L4/L4-L5/L5-S1
Use T4 - top of iliac crest as a guideline for L4 - L4-L5 space, and palpate for spinal processes
Have pt round back as mad cat
They can be sitting/lateral decubitus/prone
Wash off the area three times with iodine - let dry
Insert wheal with lidocaine and then go deeper (5 mL of 1% lidocaine = 10 mg/mL) using a 25g needle
22g Quincke needle with bevel lateral
- Prevents shearing of tissue and reduces the risk of post-dural punctual headache
The needle will pass through the supraspinous and interspinous ligament, ligamentum flavum (first pop), and Dura (second pop). At this point, remove the stylet; clear CSF should flow
Attach the syringe with medication (0.75% bupivacaine x 2 mL (15 mg), can add Astramorph (0.1-0.5mg) or fentanyl (up to 25 mcg) for pain management post-op)
Aspirate while holding the syringe and supporting hand on the back of the patient to ensure correct placement. When mixing in medication, you'll see a swirl of fluid. Inject into the subarachnoid space. Remove the syringe and needle in a smooth motion.
Monitor vital signs for possible intravascular injection (ST changes)
Place patient supine
Monitor the level of spinal
- The sympathetic level is two above the sensory level, and the motor is two below
- Check sensory with pinprick/alcohol pad for sympathetic block (temperature)
Baricity
Hyperbaric
Moves dependently with positioning
Sitting promotes saddle block
Lateral position eliminates the effect of spine curvature
Contains glucose
Hypobaric
Prone procedures
Hip procedures with affected site up, so pt does not have to lie on fracture
Contains sterile water
Isobaric
Remains in place